...
In RNA-Seq, the abundance level of a gene is measured by the number of reads that map to that gene. Once the reads have been mapped to our reference, we must now count the number of reads that map to RNA units of interest to obtain gene/exon/transcript counts. Here, we shall look at different methods for doing this.
...
Count reads mapping to genes
Get set up
...
Get set up for the exercises
| Code Block |
|---|
cds cd my_rnaseq_course cd day_3_partA/gene_counting_exercise |
...
| Code Block |
|---|
module load biocontainers
module load bedtools
type bedtools
|
The bedtools multicov command takes a feature file (GFF) and counts how many reads are in certain regions from many input files. By default, it counts how many reads overlap the feature on either strand, but it can be made specific with the -s option.
...
Let's double check this using grep.
...
To find the names of chromosomes in genome file
| Code Block |
|---|
grep '^>' ../reference/genome.fa |
| Code Block | title |
To find the names of chromosomes in gtf file
| Code Block |
|---|
cut -f 1 ../reference/genes.gtf |sort|uniq -c |
Let's fix the one chromosome that is differently named in the gtf file- mitochondrion.
...
Sed command
| Code Block |
|---|
sed 's/^dmel_mitochondrion_genome/M/' ../reference/genes.gtf > ../reference/genes.formatted.gtf cut -f 1 ../reference/genes.formatted.gtf |sort|uniq -c |
In order to use the bedtools command on our data, do the following:
| Warning | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| title | Warning: To submit to queue
|
HTseq
HTseq is another tool to count reads. bedtools has many many useful functions, and counting reads is just one of them. In contrast, HTseq is a specialized utility for counting reads. HTseq is very slow and you need to run multiple command lines in order to do the same job as what bedtools multicov did. However, if you are looking for more fine grained control over how to count genes, especially when a read overlaps more than one gene/feature, htseq-count would be an option.
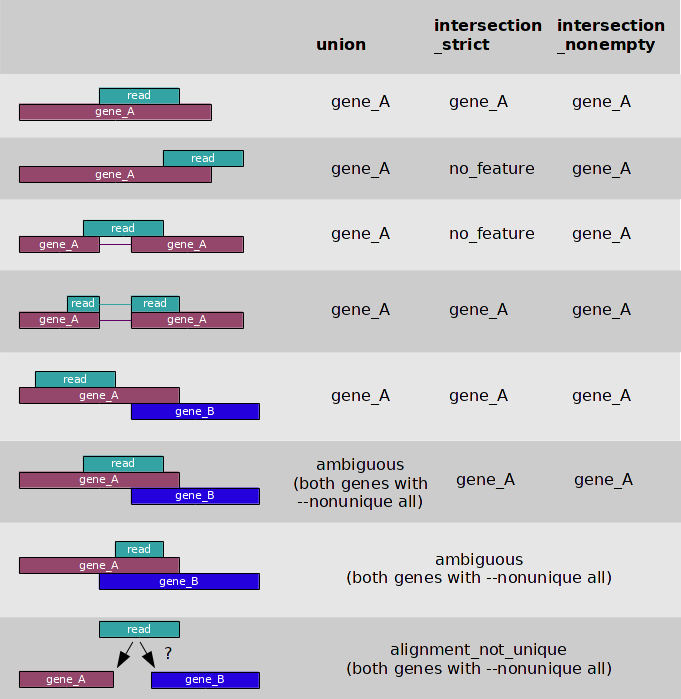
htseq-count has three modes for handling overlaps:
- mode union
mode union. This mode is recommended for most use cases.
mode intersectionmode intersection-strict.
mode intersectionmode intersection-nonempty.
Image from:http://www-huber.embl.de/users/anders/HTSeq/
What happens to the amiguous reads depends on this flag:
--nonunique none (default): not counted for any features.
--nonunique all: counted towards all.
Installing HTseq
Htseq is NOT a module on lonestar6. Module spider htseq doesn't find anything, so we have to install it.
...
Load HTseq Module
| Code Block |
|---|
module spider htseq
|
Generally, installing tools to a cluster is a pain, so avoid it if you can. However, if you have to install something, remember that you cannot install things on TACC globally, so you'll have to use options to install the tool locally to a directory that is accessible to you. Detour to how to install tools locally
1.Download HTseq source code (tar archive) from https://pypi.org/project/HTSeq/ using wget.
...
Download htseq tar and unpack it
| Code Block |
|---|
cd ~
mkdir htseq
wget https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/9b/a5/d3259656283caa0046e8d4a7e8fb1429a69a39da5c550cb259e50aafdb71/htseq-2.0.7.tar.gz
tar -xvzf htseq-2.0.7.tar.gz |
2. Build and install the tool
...
Build and install the tool
| Code Block |
|---|
cd htseq-2.0.7/
python3.9 setup.py build
python3.9 setup.py install --help
python3.9 setup.py install --user
|
3. Add the location to your PATH variable
...
Add the tool's installation location to your PATH
| Code Block |
|---|
echo $HOME #replace <yourhomedir> with YOUR HOME DIRECTORY export PATH=<yourhomedir>/.local/bin:$PATH |
IMPORTANT NOTE: By default, htseq assumes your reads are stranded and will only count the reads that map in the same direction as the feature. If you have unstranded data or if you want to count reads mapping in all directions (maybe to detect antisense genes), use --stranded no option. If you have truseq data which uses dUTP method for creating stranded libraries, your reads will actually be in reverse direction when compared to the feature. So, use --stranded reverse.
...
Let's just take a look at the commands
| Code Block |
|---|
htseq-count -m intersection-nonempty --stranded reverse -i gene_id hisat_results/C1_R1.sam ../reference/genes.formatted.gtf > C1_count1.gff
htseq-count -m intersection-nonempty --stranded reverse -i gene_id hisat_results/C1_R2.sam ../reference/genes.formatted.gtf > C1_count2.gff
htseq-count -m intersection-nonempty --stranded reverse -i gene_id hisat_results/C1_R3.sam ../reference/genes.formatted.gtf > C1_count3.gff
htseq-count -m intersection-nonempty --stranded reverse -i gene_id hisat_results/C2_R1.sam ../reference/genes.formatted.gtf > C2_count4.gff
htseq-count -m intersection-nonempty --stranded reverse -i gene_id hisat_results/C2_R2.sam ../reference/genes.formatted.gtf > C2_count5.gff
htseq-count -m intersection-nonempty --stranded reverse -i gene_id hisat_results/C2_R3.sam ../reference/genes.formatted.gtf > C2_count6.gff
join C1_count1.gff C1_count2.gff| join - C1_count3.gff | join - C2_count4.gff |join - C2_count5.gff|join - C2_count6.gff > gene_counts_HTseq.gff
#if you have many samples, use for-loop and join
|
| Warning | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Warning: To submit to queue
AFTER THIS COMPLETES:
|
Then take a peek at the results...
...
BEDTOOLS output
| Code Block |
|---|
head gene_counts.gff wc -l gene_counts.gff #If you don't have your own results yet head gene_counting_results/gene_counts.gff wc -l gene_counting_results/gene_counts.gff |
| Code Block | title |
HTSEQ output
| Code Block |
|---|
head gene_counts_HTseq.gff wc -l gene_counts_HTseq.gff #If you don't have your own results yet head gene_counting_results/gene_counts_HTseq.gff wc -l gene_counting_results/gene_counts_HTseq.gff |
HTseq-count is strand-specific in default. Therefore, read counts for each gene in gene_counts_HTseq.gff are approximately a half counts in gene_counts.gff for the corresponding gene.
...
eXpress (https://pachterlab.github.io/eXpress/manual.html) is a feature quanitification tool that is useful if you mapped RNA-Seq to the transcriptome (and didn't use a pseudoaligner like kallisto).
...
Load module eXpress
| Code Block |
|---|
module spider eXpress
module load express
type express
|
| Warning | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| title | Warning: To submit to queue
|
Other Gene Counting Options
...